- Android TextVew in Kotlin
- Android EditText Kotlin
- Android AutoCompleteTextView Kotlin
- CheckedTextView Android Kotlin
- Android Button Kotlin
- Android CheckBox Kotlin
- Android RadioGroup Example Kotlin
- Android RadioButton Example Kotlin
- Android ToggleButton Kotlin
- Android Switch Kotlin
- Android ImageView Kotlin
- Android WebView Kotlin
- Android SeekBar Kotlin
- Android CalanderView Kotlin
- Android VideoView Kotlin
- Android ProgressBar Kotlin
- Android RatingBar Kotlin
- Android SearchView Kotlin
- Android ConstraintLayout Kotlin
- Android LinearLayout Kotlin
- Android Spinner Kotlin
- Android ScrollView in Kotlin
- Android CardView Kotlin
- Android Interface Kotlin Example
- Android Airplane Mode, Bluetooth BroadcastReceiver example Kotlin
- Android Service Example
- Android Detect Phone Call BroadcastReceiver Kotlin example
- Android RecyclerView Kotlin Example
- Android RecyclerView Kotlin Example with model class
- Android sharedpreferences Kotlin Example
- Android Retrofit Example Kotlin
- Android Retrofit Example With RecyclerView
- Android Fragment Example Kotlin
- Android Auto Image Slider with URL Example Kotlin
- Android Bottom navigation Example Kotlin
- Android pdf viewer URL and Asset folder Kotlin example
- Android Audio Play Push Example Kotlin
- Scan QR Android Kotlin
- Create QR Code Android Kotlin example
- Android Collapsing toolbar Example Kotlin
- Current Location Android
- Google Map Android Example
- Search location Android kotlin
- Android Facebook login by kotlin
- View Binding Example kotlin
- Data Binding Example kotlin
- Onboarding Screen with ViewPager2 kotlin
- Android Lottie example kotlin
- Android Custom Toolbar Back Button Example kotlin
- Android Language Change example kotlin
- Dark Mode Light Mode Android Example kotlin
- Android Exit Alart Dialog kotlin
- Android Custom Dialog Popup kotlin
- Android Auto Image Slider Example kotlin
- SearchView from ArrayList kotlin
- Firebase phone authentication kotlin
- Image Download From URL and save in the folder
- Pagination in RecyclerView kotlin
- Shimmer Loading Effect kotlin
- Bottom Sheet Dialog kotlin
- Image, button transition left to right, right to left kotlin
- Voice To Text Example Android kotlin
- Image animation left to right, top to bottom Android Example kotlin
- Splash Screen Android Example kotlin
- Records audio and saves it to a folder Android kotlin Example
- Text Font add Android Example kotlin
- Take a picture from the camera set in the imageView Android kotlin
- Android Get Picture from folder set in image view kotlin
- Android Responsive Design layout for tab and phone kotlin
- Android Landscape and Portrait screen design kotlin
- Point my Current location Android kotlin
- Android Multi Select Spinner example kotlin
- Page Zoom Controls Android Example kotlin
- Dependency Injection with Dagger 2 Android kotlin Example
- Dagger Hilt Android Example kotlin
- Agora Video Audio Call Example kotlin
- Android Connect LAN printer and Print Data kotlin
- Android Connect bluetooth printer and Print Data kotlin
- DeepLink Android Example kotlin
- Socket Connection Android Example kotlin
- Web Scrapping Example in Android kotlin
- Button Click Open Gmail app and send email android kotlin example
- Firebase Email Verification Kotlin
- Button Click Text Zoom IN/OUT Android kotlin
- Zoom In /Out With Finger Touch Android kotlin Example
View Binding Example kotlin
07-Jan-2025View Binding Example kotlin
1/ Open build.gradle file ( app module) and add the following code in android block
buildFeatures{
viewBinding = true
}
below is the full code of gradle file
plugins {
alias(libs.plugins.android.application)
alias(libs.plugins.kotlin.android)
}
android {
namespace = "com.microappvalley.viewbindingkotlin"
compileSdk = 35
defaultConfig {
applicationId = "com.microappvalley.viewbindingkotlin"
minSdk = 24
targetSdk = 34
versionCode = 1
versionName = "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner = "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
isMinifyEnabled = false
proguardFiles(
getDefaultProguardFile("proguard-android-optimize.txt"),
"proguard-rules.pro"
)
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = "1.8"
}
buildFeatures{
viewBinding = true
}
}
dependencies {
implementation(libs.androidx.core.ktx)
implementation(libs.androidx.appcompat)
implementation(libs.material)
implementation(libs.androidx.activity)
implementation(libs.androidx.constraintlayout)
testImplementation(libs.junit)
androidTestImplementation(libs.androidx.junit)
androidTestImplementation(libs.androidx.espresso.core)
}
After changes to the gradle file, you must sync your project.
2/ Modify your activity_main.xml file. Add an ID on text view;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello World!"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
3/ Modify your MainActivity.kt file
package com.microappvalley.viewbindingkotlin
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.core.view.ViewCompat
import androidx.core.view.WindowInsetsCompat
import com.microappvalley.viewbindingkotlin.databinding.ActivityMainBinding
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
val binding: ActivityMainBinding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(findViewById(R.id.main)) { v, insets ->
val systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars())
v.setPadding(systemBars.left, systemBars.top, systemBars.right, systemBars.bottom)
insets
}
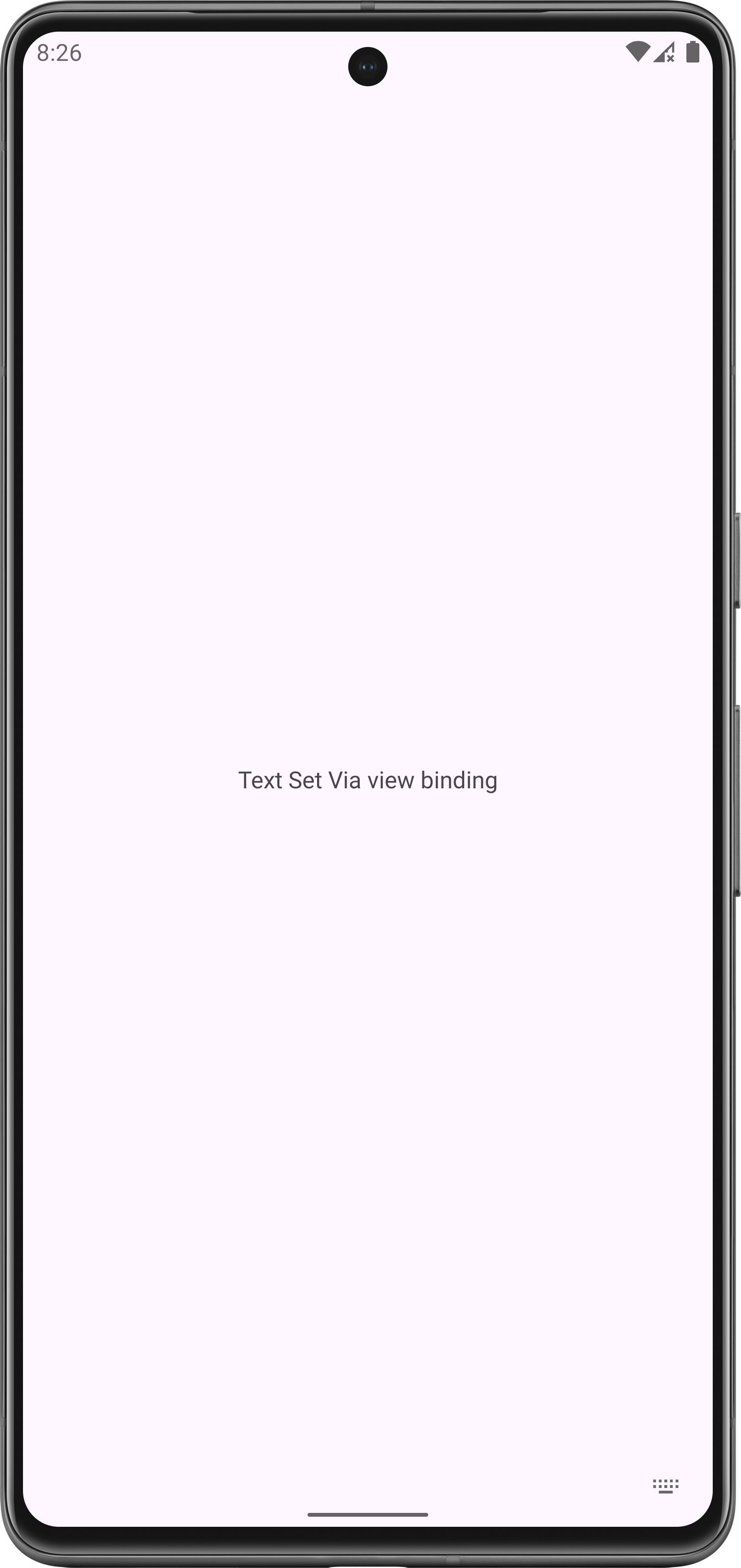
binding.textView.text = "Text Set Via view binding"
}
}
Here first you should bind your XML file.
With the view binding, automatically create a file with the same name as the XML file just adding the Binding last of the XML file
in the above example, the XML file name is activity_main
and view binding create a file name ActivityMainBinding
after getting the XML views you should set the view in the setContentView method
setContentView(binding.root)
after that, you can use views directly by binding variables without creating views variables and initializing by findViewById
binding.textView.text = "Text Set Via view binding"
Output: