
Java Inheritance
18-Sep-2024Learn how to implement inheritance in Java.
Inheritance is the process when a class inherits properties and behavior from another class.
Key Components of inheritances are:
1. Super class: The super-class whose properties and methods are inherited by another class. It also called parent class or base class.
2. Sub class: The sub-class inherits properties and methods from another class. It also called child class or derived class.
3. extends keyword: it is a keyword used for inheritance.
Syntax:
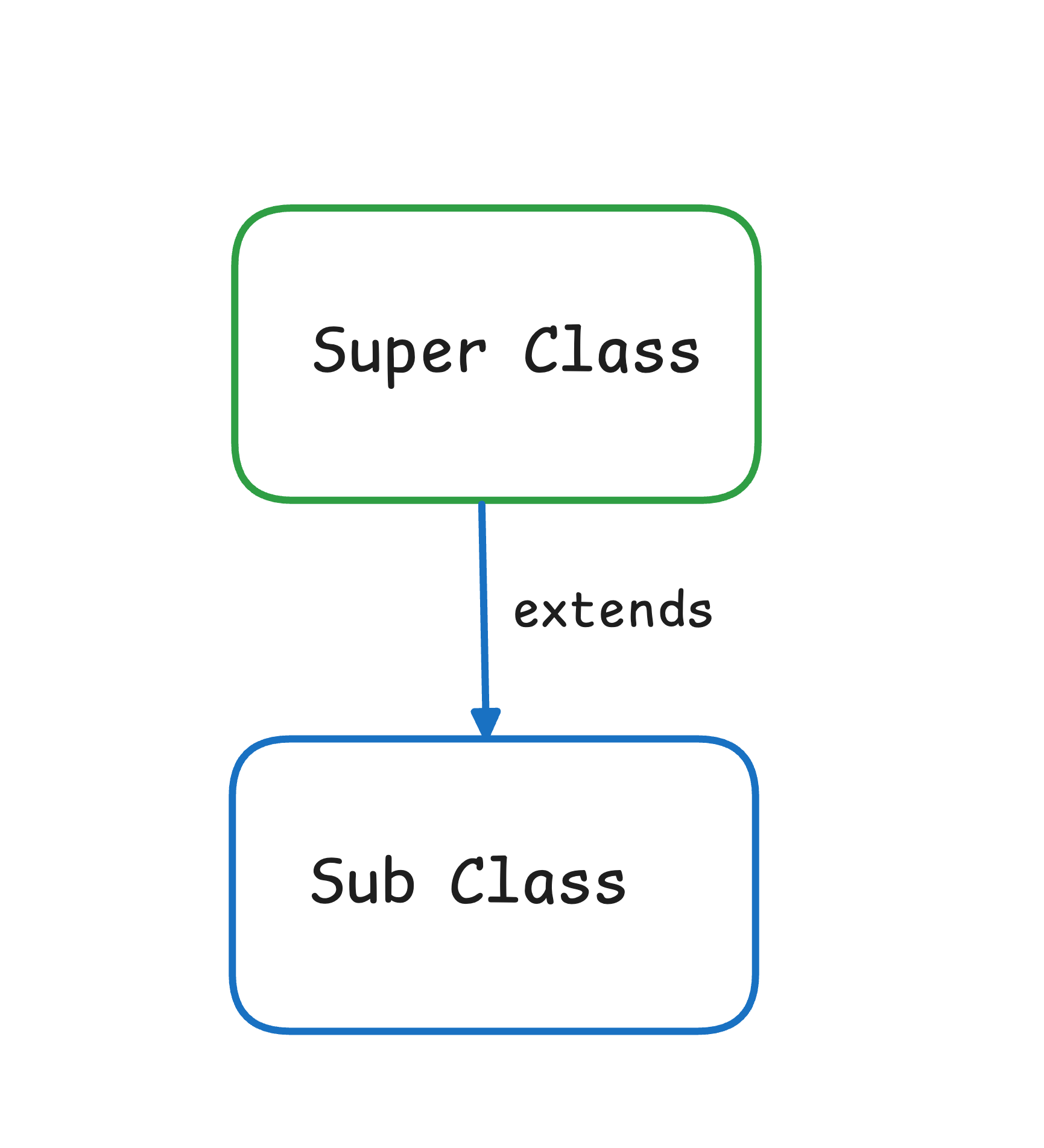
class SubClass extends SuperClass
{
// class body
}
Example:
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("This animal eats food.");
}
}
// Dog is the sub class and Animal is the super class
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("The dog barks.");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.eat(); // Inherited method eat from Animal class
}
}
Types of inheritance in Java:
1. Single inheritance : Above example is single inheritance. In single inheritance the sub class inherits a super class only.
2. Multilevel inheritance.
3. Hierarchical inheritance.
2. Multilevel inheritance: When a subclass inherits from another subclass called multilevel inheritance.
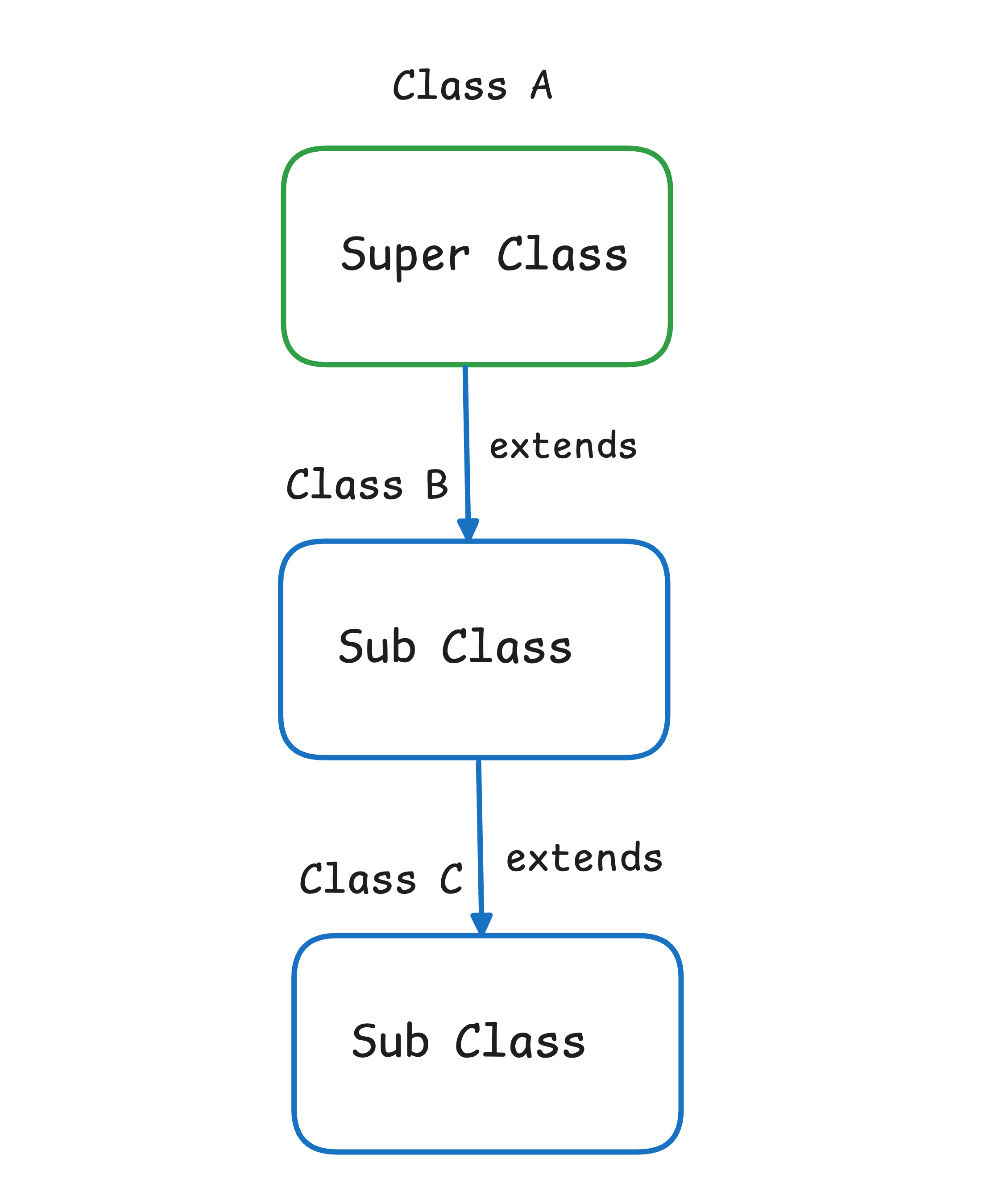
class ClassA
{
// class body
}class ClassB extends ClassA
{
// class body
}class ClassC extends ClassB
{
// class body
}
Example:
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("This animal eats food.");
}
}
// Dog Sub Class and Animal Super Class
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("The dog barks.");
}
}
// Puppy Sub Class and Dog Super Class ( which is a sub class of Animal)
class Puppy extends Dog {
void weep() {
System.out.println("The puppy weeps.");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Puppy puppy = new Puppy();
puppy.eat(); // Inherited method eat from Animal class
puppy.bark(); // Inherited method bark from Dog class
}
}
3. Hierarchical inheritance: When multiple subclass inherits from one superclass
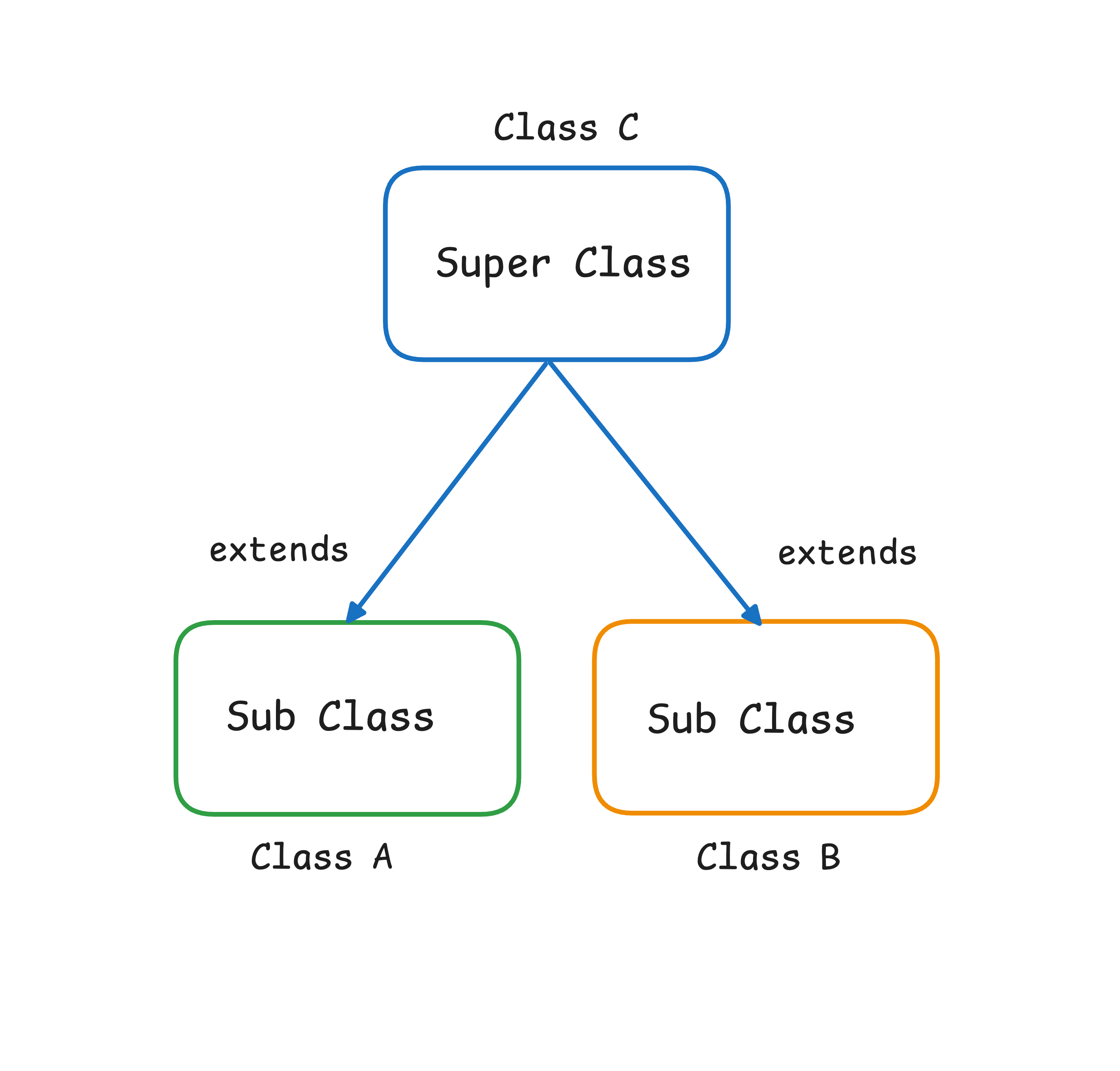
class SuperClass
{
// class body
}class SubClass1 extends SuperClass
{
// class body
}class SubClass2 extends SuperClass
{
// class body
}
Example:
// Animal Super Class
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("This animal eats food.");
}
}
// Dog Sub Class and Animal Super Class
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("The dog barks.");
}
}
// Cat Sub Class and Animal Super Class
class Cat extends Animal {
void meow() {
System.out.println("The cat meows.");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
Cat cat = new Cat();
dog.eat(); // Inherited method eat from Animal
cat.eat(); // Inherited method eat from Animal
}
}


