
Java Data Types
18-Sep-2024Explore the different data types in Java for handling various types of data.
Java has several built-in data types that are used to define the types of data that variables can hold.
Java data types can be divided into two main groups: primitive data types and reference data types.
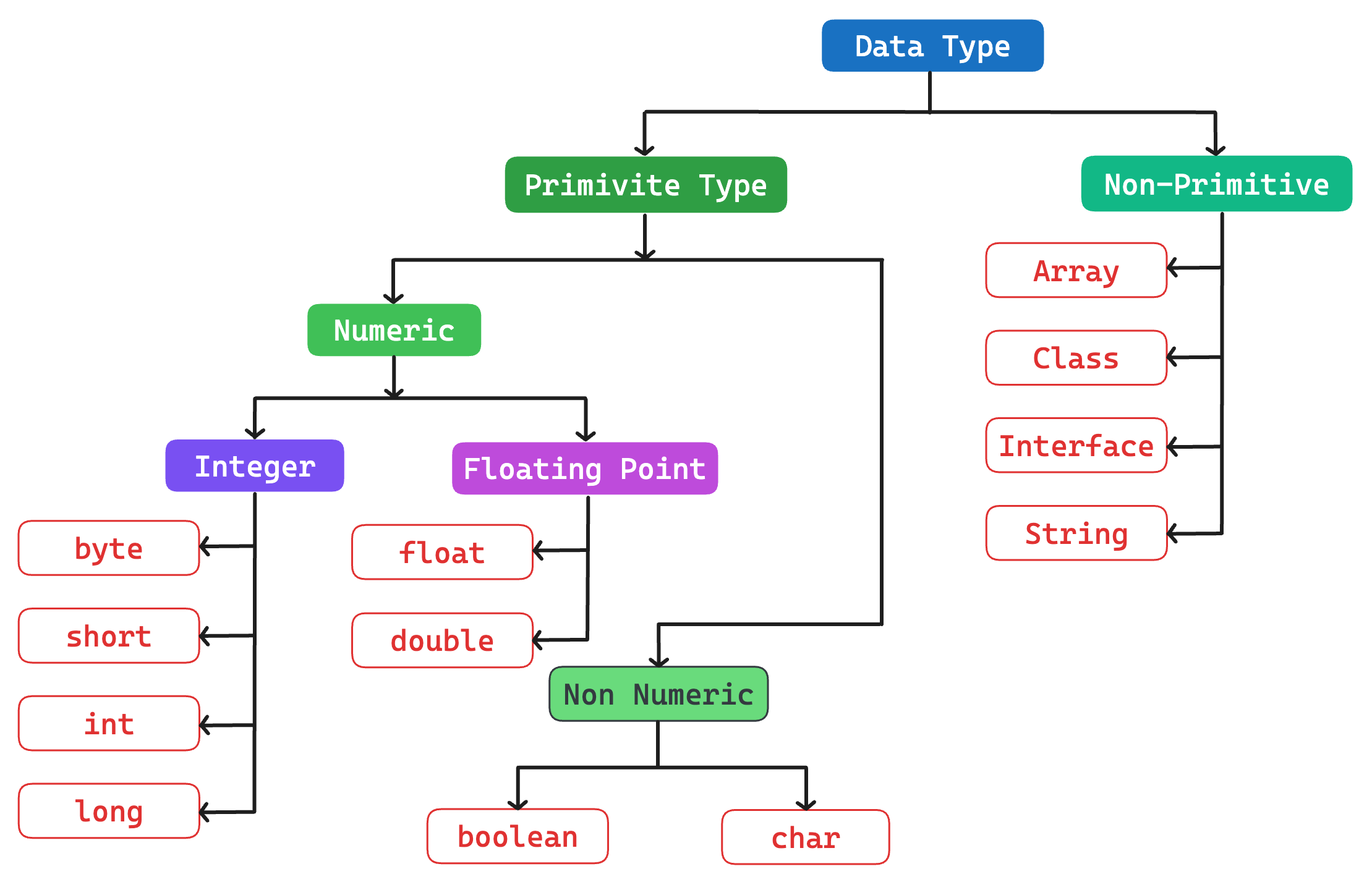
Primitive data types:
Numeric Types: Numeric Data types can not store fractions or decimal numbers.
Bytes:
Bytes:
8-bit signed integer. It is the smallest integer data type. It can store -128 to 127.
Syntax: byte byteVariableName;
Short:
16-bit signed integer. It can store -32768 to 32767.
Syntax: short shortVariableName;
int:
32-bit signed integer. It can store 2147483648 (-2^31) to 2147483647 (2^31 -1).
Syntax: int intVariableName;
long:
64-bit signed Integer. It can store -9223372036854775808(-2^63) to 9223372036854775807(2^63 -1).
Syntax: long longVariableName;
Floating point Type: It can store fractions or decimal data.
Float:
32-bit floating point. It can have a 7-digit decimal precision and the value ends with f or F like 343.345f or 235.234F. it can store
1.4e-045 to 3.4e+038 Syntax: float floatVariableName;
double:
64-bit floating point. It can have a 15-digit decimal precision.
it can store 4.9e-324 to 1.8e+308 Syntax: double doubleVariableName;
Character type:
Character type:
char:
16-bit Unicode character. It can only store a single character like a, b, H, s, etc. It can store lowercase and uppercase also. When assigned a char value must be enclosed in single quotes. We can store multiple language characters like English, Hindi, Bangla, etc.
Boolean type:
Boolean:
represents a Boolean value (true or false). it can store only true or false.
Non-Primitive data types or
Reference data types:Non-Primitive data types or
Object types:
These include the classes and interfaces you create, as well as built-in types such as String.
Array Types:
Arrays can contain elements of any data type, including primitive types and reference types. Arrays can store multiple data of the same type separated by commas (, ).
String Types:
String is a collection of characters. When assigned a char value must be enclosed in double quotes. We can store multiple language characters like English, Hindi, Bangla, etc.
Default value:
byte: 0
short: 0
int: 0
long: 0
float: 0.0f
double 0.0d
char: \u0000
boolean: false
// Primitive Data Typesbyte b = 127;short s = 32767;int i = 2147483647;long l = 9223372036854775807L; // Note the 'L' at the end to specify a long literalfloat f = 3.14f; // Note the 'f' at the end to specify a float literaldouble d = 3.14159;char c = 'A';boolean isJavaFun = true;// Reference Data TypesString greeting = "Hello, World!";int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};


